Rural Hospital Closures: How do They Impact the Country’s Economic Health?

Rural Hospitals - The Lifeblood of Local Economy
As the pandemic continued raging through the second year in a row, hospitals in rural America were the most impacted. A study by Chartis Center for rural health estimated that nearly 450 rural hospitals are facing the risk of closure.
We have a new study out this week exploring how the pandemic is increasing pressure on rural hospitals and the communities they serve as we enter year 3 of the pandemic. #ruralhealth #rural #NRHA2022 https://t.co/MZ4TCZq7ht
— The Chartis Center for Rural Health (@ChartisRural) February 10, 2022
Hospitals are the foundational keystones for most rural communities. By creating significant employment opportunities, they act as a key source of economic activity in their local communities. In fact, hospitals and healthcare providers in America employ a total of 4.5 million workers, which is not far behind the number of employees in other sectors.
Some economists estimate that the hospital industry collectively generates ~$3 trillion annually —making this industry one of the most important income sources within our society. Such figures suggest that hospitals serve as the economic anchor, if not a catalyst for growth in their surrounding communities.
So, when rural hospitals close, they impact more than just access to health care.
What are the reasons for these closures?
While some closures could be a strategic decision, the majority of the closures result from financial failures or the incapacity of these hospitals to remain profitable.
Rising uncompensated care
A 2018 study by Health Affairs reveals that a good majority of hospital closures were observed in states that did not go for Medicaid expansion. There is a possibility of Medicaid covering the finances of some low-income populations in these states. In the absence of Medicaid, this care continues to be uncompensated, causing more financial burden on the rural hospitals.
In general, a growing self-pay population and the resulting levels of uncompensated care seem to be a serious threat to the long-term survival of these critical facilities.
Higher possibility of bad debts
Small rural hospitals also face challenges with patient collections, especially from uninsured or underinsured patients. Some of these patients cannot afford the out-of-pocket expenses, while others don’t qualify for charity care. Thus, small rural hospitals lose a significant amount from bad debts, causing continuous financial stress, leading ultimately to closures.
Low occupancy
The main source of financial challenges for most rural hospitals is the diminishing population, which means low occupancy rates. This, paired with high costs, can generate unsustainable and negative margins for hospitals.
An older, sicker population
Rural America is a little bit older, a little bit sicker, a little bit poorer.
– Anand Parekh M.D., Chief Medical Advisor, Bipartisan Policy Center, as quoted in the Advisory Board Daily Briefing (March 3, 2018)
Rural hospitals provide healthcare to a population that is older, poorer, and sicker than national averages. As a result, the cost of care is more than what they can recover. This causes a significant surge in operational expenses that most hospitals are unable to sustain.
Hospital Closures and Their Impact on Life
Over 100 rural hospitals closed their doors between January 2013 and February 2020. As iterated already, hospital closures could have a far-reaching impact on various facets of life.
Delayed access to essential healthcare
Hospital closures, especially in rural areas, can create hospital “deserts” where patients will have to commute long distances for essential medical services.
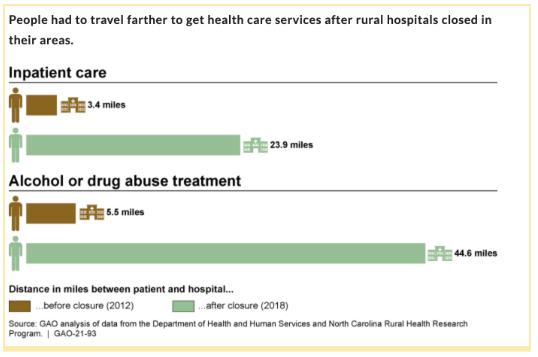
Image source - GAO.gov
For anyone living in the city, the fastest access to healthcare is just a short drive away. But this is not the case for the rural population of America. There are regular stories of elderly adults having to drive for at least 5 hours to the nearest health facility, even in times of emergency.
Now, an extended trip to the nearest hospital can cause life-threatening scenarios, especially during emergencies. Patients may also face other health implications due to limited or delayed access to professional medical assistance.
A 2016 study by the Kaiser Commission on Medicaid and the Uninsured found that long commutes and extended travel time resulted in increased delays or forgone care, particularly among the elderly and low-income groups.
Also Read: The Digital Front Door - Why Does Your Health Facility Need One?
No access to specialist practitioners
When hospitals close, it can lead to the relocation of doctors and health practitioners in search of better opportunities. This leaves a void in the community when it comes to access to vital care and treatment for important health conditions such as mental health or substance abuse. Further, retention of healthcare professionals such as nurses, midwives or physician assistants is an ongoing challenge for rural hospitals. Thus, access to primary care is hindered.
Increase in unemployment
Healthcare sector remains the backbone of economic activity in rural areas, providing economic stability and job opportunities in the communities. In many parts of the country, hospitals are the largest employers. So when hospitals close, all those employed by these hospitals are left jobless. Also, when hospitals close, pharmacies and other related medical services shut down or move to other communities. And so do other non-medical businesses depending on them, like restaurants, grocers etc.
The Chartis report that we cited earlier claims that if the vulnerable hospitals were to close, it could lead to the loss of at least 137,000 community jobs.

Sustainability of Rural Hospitals - A Crisis in the Making
A study by The Chartis Center for Rural Health reported that 44% of rural providers witnessed a negative operating margin in part due to high rates of uninsured populations in rural communities.
A report by Beckers Hospital Reviews gives the state-wise breakdown of nearly 897 rural hospitals across America on the verge of closure. The report reveals that at least 25% of rural hospitals are facing the risk of immediate closure in 22 states.
These reports highlight the sorry state of sustainability that most hospitals are experiencing.
Rural hospitals must thus, find a way to operate more efficiently - especially as uncompensated care is on the rise.
Many rural hospitals opt for mergers or join regional health groups. Other hospitals will need to start implementing effective solutions like CoverMe to help reduce uncompensated care.
Leveraging Technology to Tide Over the Challenges
Technology is vital for hospitals. Many hospitals are turning to integrated technology solutions like CoverMe to streamline their front-end revenue cycle operations, provide digital tools for their front-desk staff to automate coverage verification and eligibility determination, and simplify patient collections.
CoverMe is the industry leader in addressing uncompensated care and offers hospitals and patients a wide range of solutions for front-end revenue cycle management. Talk to us to learn more about how technology could benefit your hospital or healthcare organization's bottom line. Schedule a demo today with CoverMe!


