Difference between Medicare and Medicaid
Medicare vs Medicaid: What’s the difference?
Medicare and Medicaid are insurance programs that are designed to benefit the people of the United States in various ways. In simple words:
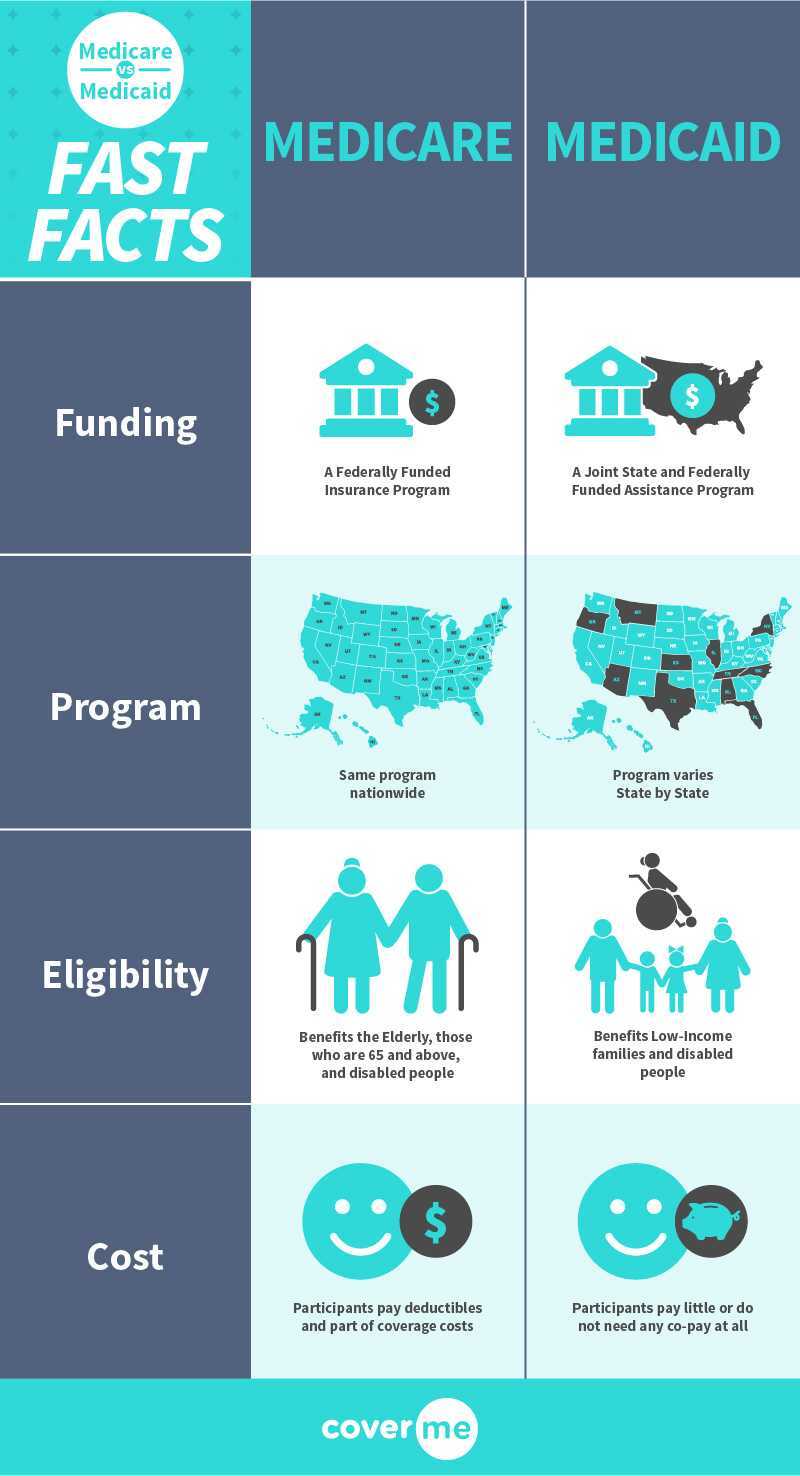
- Medicare is a federal health insurance program for persons who are over 64 years of age, persons with renal diseases, and certain younger people with disabilities.
- Medicaid is for people who fall under particular low-income criteria.
The two terms Medicare and Medicaid are often confused or used. These two programs sound extremely similar but have vastly different schemes.
In this article, we will be talking about the various benefits of Medicare and Medicaid while also speaking about various other articulates that revolve around those two terms.
Key things to know about Medicare and Medicaid
What Is Medicare?
Medicare is a national health insurance program in the United States that was established in 1965. It was under the Social Security Administration and is now administered by the Centres for Medicare and Medicaid Services which is an agency of the federal government.
Medicare plays a pivotal role in helping people with disabilities. Medicare also provides health and financial security to 60 million older people in the United States. It covers many basic health services such as hospital admission, physician services and prescription drugs.
There are two branches that stem from the umbrella of Medicare.
- Original Medicare – A government-funded medical insurance program that many older Americans use.
- Medicare Advantage – This is an insurance option for people who want the Original Medicare but with more coverage choices available on the table.
What Is Medicaid?
Medicaid is a public health insurance/ assistance program in the United States that is a joint federal and state program. It provides effective health coverage to low-income individuals of all ages. Medicaid is available only to those families that meet the low-income criteria which vary from state to state.
Eligibility of Medicare vs Eligibility of Medicaid
Who is eligible for Medicare?
People above the age of 65 will be served primarily and their medical bills are paid from trust funds, whatever their income. It also serves younger people, under 65, who are disabled and have undergone / are undergoing dialysis (people who are receiving Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) for a certain amount of time, or and with End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)).
Also Read: Get ready for the Medicaid cliff
Who is eligible for Medicaid?
Medicaid is eligible for U.S Immigrants, permanent residents or legal immigrants. As of September, 2020, Close to 70.6 million people were covered by Medicaid. Medicaid provides health coverage to:
- children
- pregnant women
- seniors citizens and
- individuals with disabilities who have limited resources and income.
The eligibility qualifies for free or low-cost care for the people of the United States based on the family’s income and size while medicaid happens to be the single most largest source of health coverage in the United .
Coverage of Medicare and Medicaid
What does Medicare Cover?
Medicare program consists of several parts that offer coverage to different aspects of healthcare. Details are listed in the table below:
| MEDICARE PART – A | Provides coverage for many inpatient medical care such as hospital stays, hospice services, limited skilled nurse care and home healthcare. |
| MEDICARE PART – B | Provides coverage for outpatient medical care such as for items and services including outpatient hospital care, physician appointments, preventive care and for certain medical equipment. |
| MEDICARE PART – C OR MEDICARE ADVANTAGE | Is run by approved private insurers that includes all the benefits of parts A and B while also including benefits for an extra cost like dental, vision and prescribed drug coverage. |
| MEDICARE PART – D | Is run by approved plans according to federal rules and helps pay for prescribed drugs. |
What does Medicaid Cover?
Medicaid programs’ benefits vary from state to state but there are few benefits included in every program as listed below:
- Lab and X-ray services.
- Inpatient and outpatient hospital services.
- Family planning services like birth control, nurse and midwife services.
- Health screening and applicable medical treatments for children.
- Nursing facility services for adults.
- Surgical dental services for adults.
Since Medicaid varies from state to state, it is always advised to consult with a caseworker in each state to get to know about the coverage that applies.
How to apply for Medicare vs How to apply for Medicaid
How To Apply For Medicare?
Getting a Medicare plan could be a rather major milestone. Here’s a heads-up to get started on that journey.
-
- Some people get Medicare automatically, and some will have to sign up in that case, people who are 65 or almost 65 and not receiving Social Security.
- There are certain times of the year when one can sign up or change how one gets their coverage.
- Signing up for Medicare Part B when first eligible will be easier to avoid penalties in the future.
- It is not a necessity to sign up for Medicare every year, rather, each year there will be a chance to review coverage and can also enable changing of plans.
How To Apply For Medicaid?
There are two ways to apply for Medicaid:
-
- Contact your State Medicaid Agency – It requires the applicant to be a resident of that particular state.
- Filling out an application through the Health Insurance Marketplace.
Cost Of Medicare v Cost of Medicaid
What are the costs of Medicare?
In the table below, the costs of Medicare are broken down into four parts:
| Part A premium | Most people don’t pay a monthly premium for Part A . If you buy Part A, you’ll pay up to $471 each month in 2021. If you paid Medicare taxes for less than 30 quarters, the standard Part A premium is $471. If you paid Medicare taxes for 30-39 quarters, the standard Part A premium is $259. |
| Part A hospital inpatient deductible and coinsurance | You pay: $1,484 deductible for each benefit period Days 1-60: $0 coinsurance for each benefit period Days 61-90: $371 coinsurance per day of each benefit period Days 91 and beyond: $742 coinsurance per each “lifetime reserve day” after day 90 for each benefit period (up to 60 days over your lifetime) Beyond lifetime reserve days: all costs |
| Part B premium | The standard Part B premium amount is $148.50 (or higher depending on your income). |
| Part B deductible and coinsurance | $203. After your deductible is met, you typically pay 20% of the Medicare-approved amount for most doctor services (including most doctor services while you’re a hospital inpatient), outpatient therapy, and durable medical equipment (DME) |
| Part C premium | The Part C monthly premium varies by plan. Compare costs for specific Part C plans. |
| Part D premium | The Part D monthly premium varies by plan (higher-income consumers may pay more). Compare costs for specific Part D plans. |
Source: https://www.medicare.gov/your-medicare-costs/medicare-costs-at-a-glance
What are the Costs Of Medicaid?
According to a recent analysis, National Healthcare Expenditure (NHE) grew 4.6% to $3.8 trillion in 2019. That makes it $11,582 per person. States have the liberty to charge premiums and cost-sharing for Medicaid enrollees.
Medicaid also kicks in for seniors on Medicare whose income is insufficient to cover premiums, deductibles, and other insurance costs.
In cases of emergency services, family planning requirements, pregnancy-related and some preventative services for children, Medicaid offers zero costs and co-pays.
Also Read: Hospitals Expected to Take a Hit
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Medicare?
As discussed above, every coin has two sides and so does Medicare. Here’s a short analysis of the pros and cons of Medicare.
Advantages of Medicare
- Medicare provides coverage to those who wouldn’t have coverage otherwise as they couldn’t afford it.
- The costs are very little, out-of-the-pocket amounts every month.
- Medicare’s Advantage plans offer additional coverage to older Americans who would suffer otherwise.
- Medicare has led to innovations in the field of pharmaceuticals where companies had more opportunities to develop prescription drugs.
- Medicare has enabled a massive increase in medical standards.
Disadvantages of Medicare
- The costs of Medicare are a huge amount to administrate for the healthcare system.
- People with poor or worse health conditions had out-of-pocket costs two times higher than the healthier beneficiaries.
- The hospital stay costs gradually go higher for people who are under preventable conditions placing an increased burden on hospitals.
- A surge in opioid related crimes and fraudulent doctors. These doctors billed Medicare for drugs that were never purchased in the first place,
- New York Times reported.
- Medicare costs taxpayers a huge amount.
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Medicaid
Both the pros and cons of Medicaid vary from situation to situation and we have listed down few highlights below.
Advantages of Medicaid
- Senior citizens and people with disabilities have known to account for approx. two thirds of medical aid spending in America.
- The costs are much more affordable and lower while some procedures do not need any co pay at all.
- People with a financial constraint won’t be burdened with huge hospital bills since Medicaid guarantees financial protections.
- Private care plans are also easily accessible by people who are covered under Medicaid.
Disadvantages of Medicaid
- Since Medicaid varies from state to state not all low-income individuals will benefit from Medicaid.
- In worst case scenarios, when people tend to end up for an emergency procedure, they might have to undergo compromise-able treatment just because they are covered under Medicaid.
- Individuals who come under Medicaid plans are prone to discrimination.
- Few procedures are exempted from the books of Medicare while making it hard for people who need such procedures but couldn’t afford to do them anyway.


